5 connectivity and computing themes shaping the future—insights from MWC & EW 2025
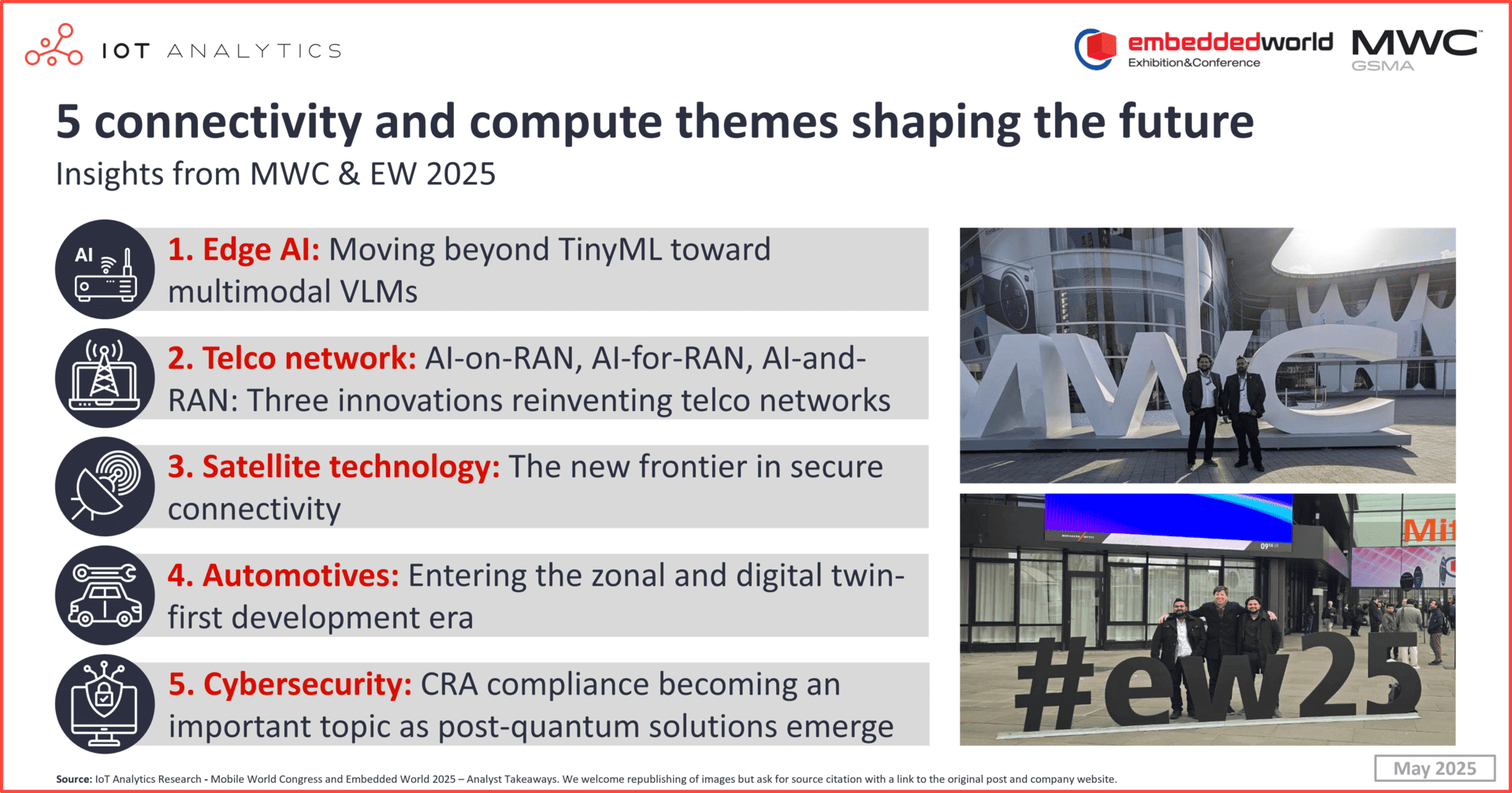
In short
- Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025 and Embedded World (EW) 2025 spotlighted key telecom and embedded system trends.
- AI, connectivity advancements, future vehicle architectures, and security were central themes.
- IoT Analytics had teams on-site to track the evolution of networks, edge computing, and embedded intelligence.
- This article summarizes 5 key themes from both events. The full 101-page MWC & EW 2025 event report with numerous detailed examples is available exclusively to IoT Analytics customers.
Why it matters
- Mobile World Congress and Embedded World are the most important exhibitions for their relative fields: connectivity and embedded systems. Many cutting-edge technologies showcased at such events become the industry standard a few years later.
The insights from this article are based on
Mobile World Congress and Embedded World 2025—Analyst Takeaways
A 101-page report presenting the key highlights, trends, and in-depth insights from the Telco and Embedded communities assembled by the IoT Analytics’ analyst team at MWC 2025 & Embedded World 2025.

Already a subscriber? View your reports here →
About Mobile World Congress and Embedded World 2025
Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025 and Embedded World (EW) 2025 highlighted critical developments across telecom and embedded industries, as shown in IoT Analytics’ 101-page Mobile World Congress and Embedded World 2025—Analyst Takeaways report (published April 2025).
IoT Analytics had a team of analysts on-site at both events. The team visited over 120 booths, conducted over 50 interviews, and attended multiple closed-door sessions. The full 101-page event report provides in-depth insights, including vendor comparisons, highlights from keynote speeches, important announcements, and major trends identified by the team.
About MWC 2025
MWC 2025 held in Barcelona, Spain, between the 3rd and 6th of March 2025, a strong interest in telecom was on display , with participation back to pre-pandemic levels. The event drew 109,000 visitors, an increase of 8% over 2024. Exhibitor numbers reached a record 2,900. Key topics included 5G expansion, network automation, satellite connectivity, AI integration, and early preparations for 6G networks.
During a presentation on the state of 5G at MWC 2025, GSMA shared that 326 out of 783 global operators have now launched 5G networks , with a $70 billion revenue opportunity expected by 2030. AI use cases are reshaping network demands, driving the need for lower latency and more deterministic performance.
About EW 2025
EW 2025 held in Nuremberg, Germany, between the 11th and 13th of March 2025, reflected the growing role of AI and IoT in embedded systems. Visitor numbers remained stable at around 32,000, while exhibitor numbers rose by 18% compared to pre-pandemic levels, setting a new record. The event showed a shifting focus toward real-time edge AI, secure embedded software, next generation vehicle architectures, and quantum-resistant security.
Competition is intensifying at the chipset level, with companies like Altera positioning field-programmable gate arrays (or FPGAs) as a flexible, high-performance choice for edge AI.
5 connectivity and compute themes shaping the future
Below, the team shares 5 key themes shaping the future of secure connectivity and computing based on their observations at both events:
1.Edge AI: Moving beyond TinyML toward multimodal VLMs
Edge AI evolves with multimodal models and industrial-grade deployments. Edge AI is entering a new era, moving beyond TinyML models to running fully-fledged multimodal large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) directly on industrial-grade edge devices. Reflecting this broader evolution, the TinyML Foundation itself rebranded as the Edge AI Foundation in November 2024—an acknowledgment that the edge AI landscape now encompasses far more than ultra-small models. While last year’s EW focused heavily on “AI coming to the edge,” MWC and EW 2025 showcased live, real-world deployments that demonstrate edge AI has firmly arrived.
Three simultaneous shifts are driving this transformation:
First, AI accelerators have become significantly more powerful and efficient. Accelerator platforms like US-based Qualcomm’s Cloud AI 100 Ultra and US-based AMD’s Instinct MI210 now support real-time inference for models with billions of parameters—all while meeting industrial latency and thermal constraints. For example, at EW 2025, Taiwan-based embedded intelligence platforms technology company Advantech demonstrated chat interfaces and live video analysis using LLMs run entirely on-site with its AIR-540 system running on AMD’s Ryzen and EPYC processors paired with AMD Radeon GPUs and Instinct MI210 accelerators.

Advantech demonstrates edge AI solutions powered by AMD for real-time, local processing (source: IoT Analytics at EW 2025)
While hardware platforms such as the Cloud AI 100 Ultra are capable of running models up to 100 billion parameters, most real-world edge deployments today focus on compact 3B–8B models to optimize latency, cost, and energy efficiency.
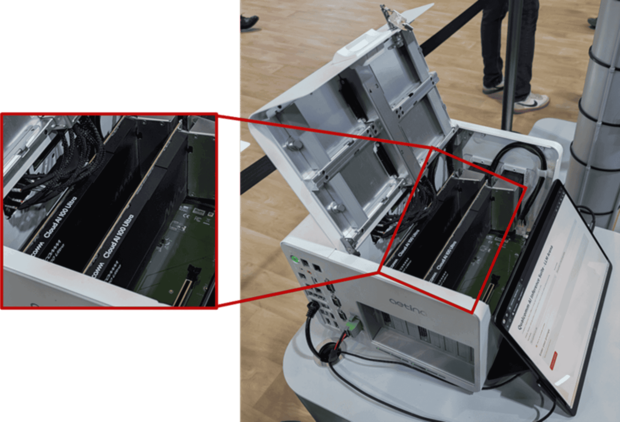
Dual Qualcomm Cloud AI 100 Ultra cards mounted via PCIe in US-based edge AI solutions provider Aetina’s MegaEdge AIP-FR68 edge AI IPC (source: IoT Analytics at EW 2025)
Second, the LLMs and VLMs themselves are becoming more edge-optimized. Architectural innovations like China-based AI research lab DeepSeek’s R1 model and other lightweight multimodal models are enabling powerful inference at a fraction of previous computational requirements. Critically, zero-shot VLMs are starting to reshape edge applications such as AI-based video surveillance. For example, at MWC 2025, South Korea-based mobile network operator LG U+ and US-based AI-powered technology solutions company IXI—in partnership with South Korea-based edge AI semiconductor company DeepX—demonstrated edge gateways capable of detecting abnormal events (like “A pot on the induction cooktop is catching fire” or “Someone helps an old man who is falling down”) without any custom model training—unlocking new possibilities for safety, industrial monitoring, and smart cities.

Example of IXI and LGU+’s abnormal events detection system, with a kitchen fire and fall highlighted (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
Third, the edge AI ecosystem is rapidly maturing on the software side. Vendors are now offering comprehensive software frameworks that manage the full lifecycle of edge AI—from model training and optimization to deployment, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and runtime management. Examples include:
- Qualcomm with its recent Edge Impulse acquisition and model pipeline training integration
- Fibocom and SIMCom, both China-based wireless module suppliers, with their integrated AI software stack s
- Infineon, a Germany-based semiconductor manufacturer, with its DEEPCRAFT Studio, formerly Imagimob Studio
These software stacks dramatically reduce the time and effort required to bring AI-powered solutions to production at the edge.

SIMCom and Fibocom AI stacks emphasizing the integration from modules to models for optimizing edge AI deployment and model conversion (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
2. AI-on-RAN, AI-for-RAN, AI-and-RAN: Three innovations reinventing telco networks
AI transforms radio access networks (RAN) to enable low-latency applications. RAN is emerging as a critical zone for AI-driven innovation in telecommunication. To meet growing demands for real-time applications and to manage escalating network complexity, telecom operators are embedding AI into the RAN in three distinct ways: on, for, and with the RAN.

HPE highlights AI-RAN Alliance and AI classifications for RAN integration: AI for RAN for efficiency and scheduling, AI and RAN for shared computing infrastructure, and AI on RAN for GenAI and private 5G applications (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
AI on RAN
AI on RAN refers to using RAN infrastructure to run AI models for end-user applications, directly at the network edge. By deploying AI inference engines close to users, operators enable ultra-low latency applications such as autonomous robotics, industrial monitoring, and AR/VR.
At MWC 2025, Japan-based information and communications technology company Fujitsu demonstrated its AI on RAN solution, embedding AI directly into the RAN to improve latency-sensitive applications. In a robotics use case, AI inference at the edge enabled successful real-time target tracking, compared to cloud-based AI that resulted in high latency and failed tracking. The solution used Japan-based telecommunications company SoftBank Corp.’s AITRAS reference architecture and US-based AI platform and semiconductor company NVIDIA’s GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip to run AI locally at the network edge, optimized for compute-intensive tasks like object tracking and video analysis .

Fujitsu’s AI-on-RAN demo showing that cloud-based AI can lead to 200ms latency, causing failure; however, embedding AI within RAN achieves real-time success in robotic target tracking (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
AI for RAN
AI for RAN marks the transition toward intent-based networking with early deployments of agentic AI supporting RAN optimization. Unlike traditional manual RAN management, AI for RAN uses intelligent agents to interpret operator intents and autonomously reconfigure the network. At MWC 2025, Germany-based telecommunications company Deutsche Telekom and US-based hyperscaler Google Cloud showcased RAN Guardian, an AI agent that autonomously detects network anomalies and applies corrective actions in real time. Similarly, Sweden-based telecommunications and networking technology company Ericsson and Norway-based telecommunications company Telenor demonstrated an agentic AI proof-of-concept that dynamically adjusts mobile network settings to balance energy efficiency and capacity, achieving a 4% reduction in energy consumption.
One of the most instructive examples at MWC 2025 comes from Japan-based telecommunications company KDDI, where an AI agent engaged with an operator via chat to optimize a RAN deployment for a high-traffic fireworks event. The AI agent successfully interpreted event details and suggested additional optimizations, such as supporting electronic payments—going beyond merely executing commands to offering operational insight.
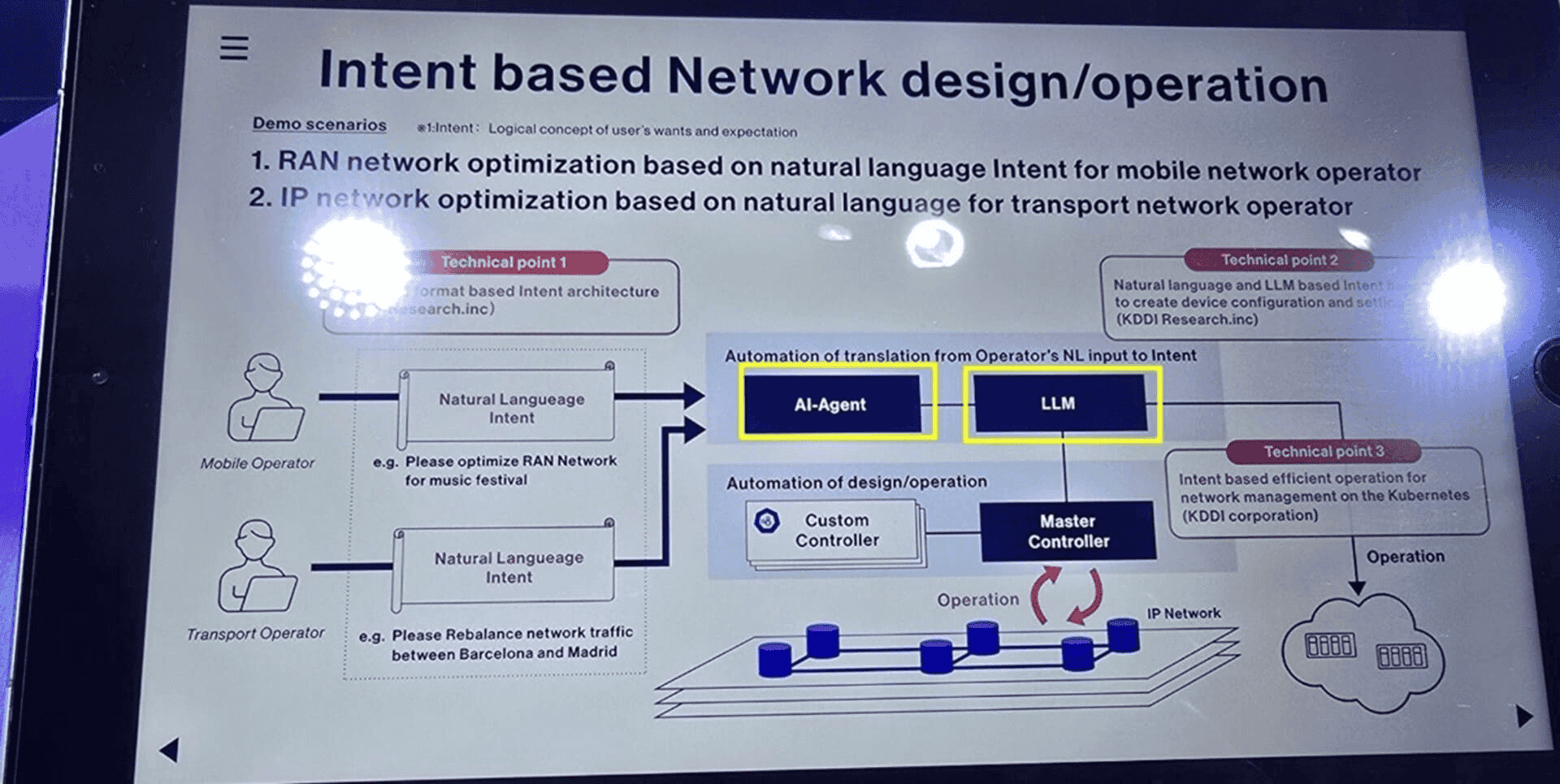
KDDI showcasing how agentic AI and LLMs translate operator intent into automated network design and operations for RAN and IP networks (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
Key analysis from the MWC and EW 2025 events report:

“AI agents in RAN optimization shows early signs of intelligent assistance, but full automation remains elusive. Although agents contribute operational insights, current systems still require two layers of human oversight—technical validation and business-level confirmation—before execution. This highlights the organizational and policy-driven barriers that prevent full closed-loop automation today.”
– Satyajit Sinha, Principal Analyst at IoT Analytics
AI and RAN
AI and RAN envisions hybrid platforms where both end-user AI applications and RAN optimization AI run on shared, cloud-native infrastructure. While promising for reducing infrastructure duplication and enabling cross-domain orchestration, real-world deployments are still nascent. US-based IT infrastructure company Dell and Finland-based telecommunications and IT company Nokia presented joint concepts at MWC 2025, highlighting early experiments in AI and RAN co-location at the network edge.
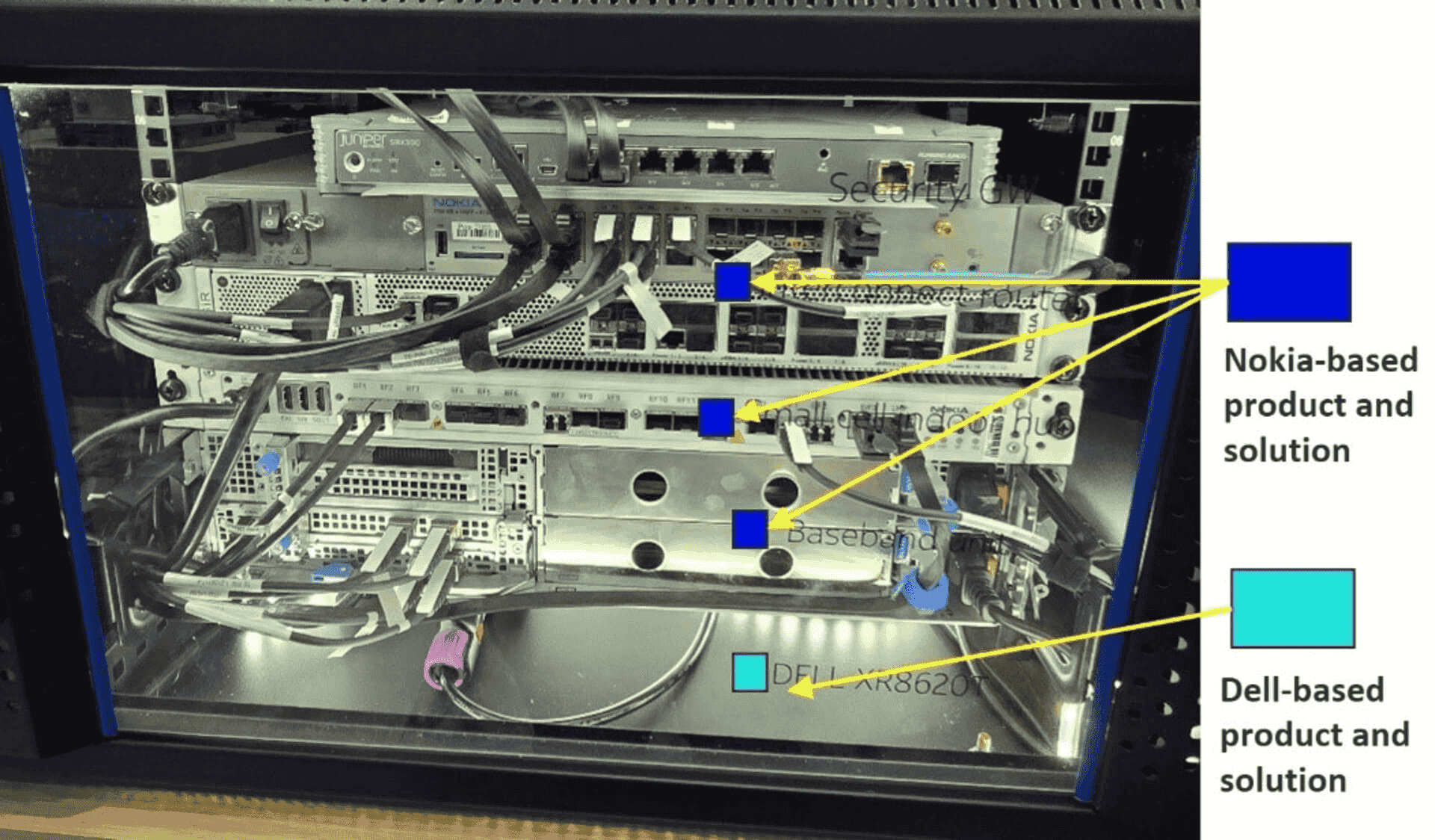
Hardware view of the integrated Dell–Nokia edge solution, highlighting Nokia’s small cell radio and baseband alongside the Dell XR8620 edge server—demonstrating the physical convergence of private wireless and edge compute infrastructure (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
3. Satellite technology: The new frontier in secure connectivity
Satellite networks enhance connectivity for disaster recovery and remote sites. Satellite networks are rapidly moving from being a backup layer to becoming a core part of terrestrial connectivity strategies. At MWC, multiple vendors demonstrated how satellite systems are reshaping telecom, IoT, and industrial deployments.
Satellite as cellular backhaul is now an operational reality. At MWC2025, KDDI showcased live deployments where US-based space telecommunications company Starlink’s satellite constellations provide resilient cellular backhaul for rural areas and other low-coverage places, such as natural disasters where where fiber and other backhaul-dependent cellular towers may be down, ensuring critical communications in emergency zones. This positions LEO constellations as vital tools for disaster recovery and rural network extension, offering redundancy in hybrid terrestrial-satellite architectures.
Satellite-private 5G networks are also emerging. Also at MWC2025, Luxembourg-based communication satellite company SES and US-based telecommunications infrastructure provider Globalstar separately presented architectures where enterprises can deploy private 5G networks with satellite uplinks, bypassing the need for terrestrial fiber connections. This unlocks connectivity for remote industrial sites, offshore platforms, energy infrastructure, and isolated mining operations—sectors historically underserved by traditional networks.
Quantum-safe satellite communications are advancing as well. Spain-based telecommunications company Telefónica and Italy-based quantum-based communications solutions company ThinkQuantum separately showcased pilots where satellites play an active role in securing critical communications at MWC 2025. One notable project is EAGLE-1, Europe’s first satellite-based quantum key distribution system. Developed by ThinkQuantum in partnership with SES, the European Space Agency, and the European Commission, EAGLE-1 uses optical quantum communication between satellites and ground stations to generate encryption keys that are immune to both quantum and classical attacks. This initiative aims to create a secure, large-scale communication framework for governmental and critical infrastructure applications across Europe.
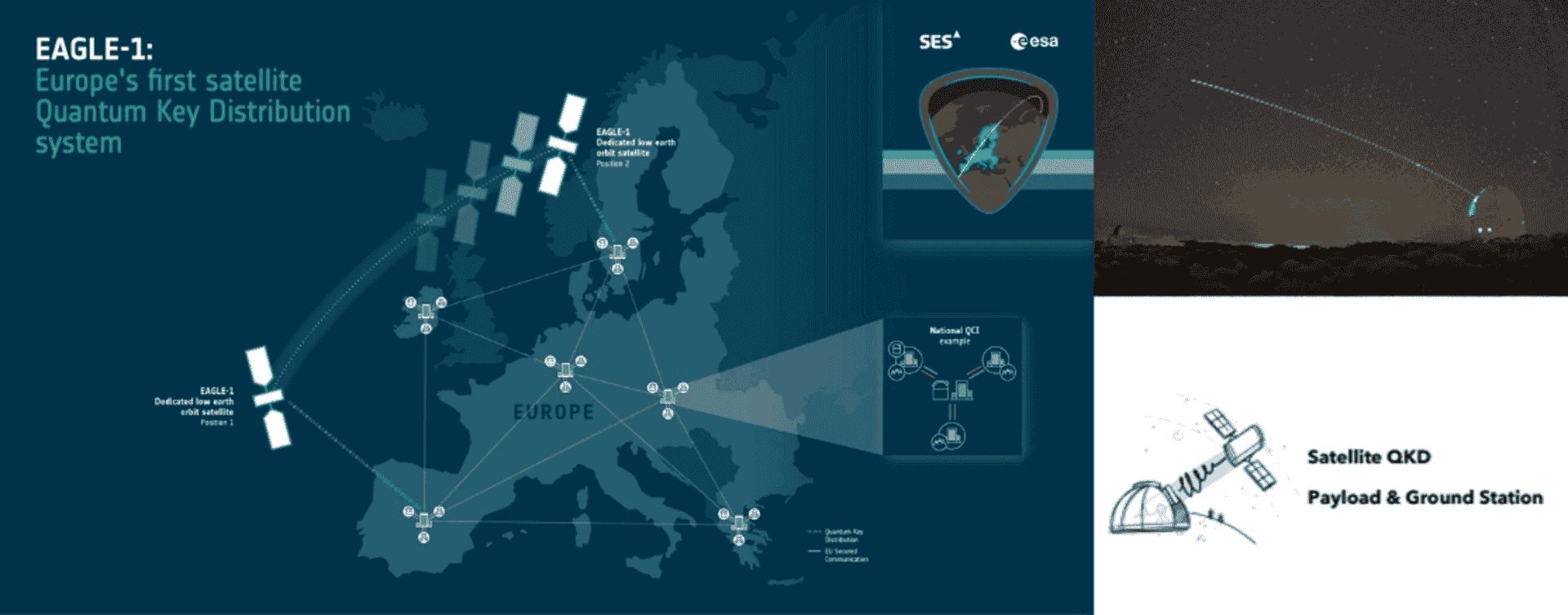
Graphics illustrating how EAGLE-1 uses optical light-based communication technology, based on ThinkQuantum, between satellites and ground stations to securely generate keys that ensure quantum-safe encryption for Europe’s data networks (source: European Space Agency)
4. Automotives: Entering the zonal and digital twin-first development era
The automotive sector is entering a transformational phase as vehicles move from distributed, domain-based architectures to zonal computing architectures—laying the foundation for fully software-defined vehicles (SDVs). At MWC 2025 and EW 2025, hardware and software vendors demonstrated how next-generation automotive platforms are being designed and validated.
Zonal controllers are becoming the cornerstone of vehicle compute architectures. At EW2025, semiconductor vendors Infineon, Netherlands-based NXP, and Switzerland-based STMicroelectronics all launched MCU/MPU platforms (AURIX TC4x, S32K5, and Stellar G6, respectively) specifically optimized for deterministic networking, fine-grained hardware isolation, and hypervisor-enabled mixed-criticality support. These zonal controllers enable fail-operational Ethernet rings and time-sensitive networking across safety-critical domains such as lighting, steering, braking, and advanced driver assistance systems.
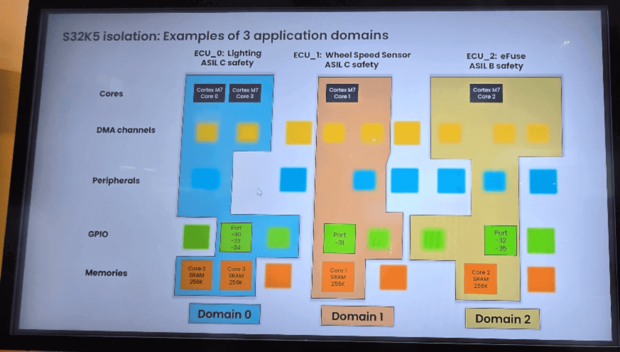
NXP showing how the S32K5’s domain-based isolation approach integrates multiple ASIL-rated ECUs on one MCU by isolating cores, memory, and I/Os per application (source: IoT Analytics at EW2025)
Digital twins are enabling virtual-first software development, and it is reshaping how vehicles are engineered. At MWC 2025 and EW 2025, vendors demonstrated that pre-silicon, virtual-first methodologies are no longer optional but essential. Germany-based industrial automation company Siemens, in collaboration with US-based hardware and software company Microsoft and AMD, showcased its PAVE360 platform at EW 2025—a full-stack simulation environment that enables cloud-based SDV development from algorithm modeling to virtual system-on-chip validation and real-time synchronization with physical prototypes.
Also at EW 2025, Vector Informatik, a Germany-based software developer for networked electronic systems, and Synopsys, a US-based electronic design automation company, demonstrated how virtual electronic control units (ECUs) can now integrate into full continuous integration/continuous deployment workflows, allowing software teams to test and validate automotive software stacks long before physical test hardware is available.
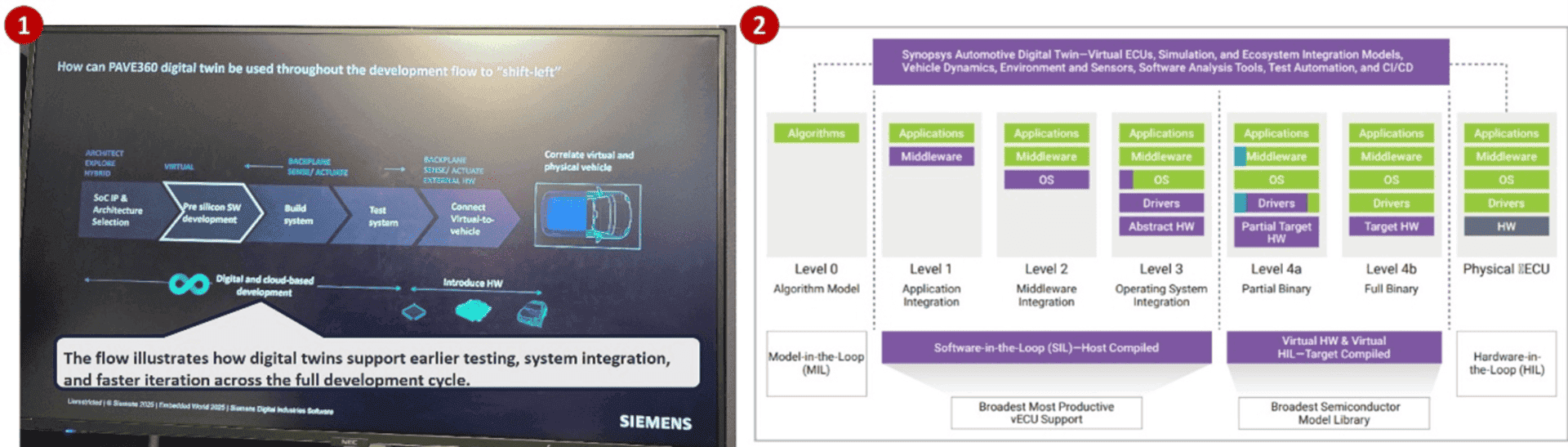
1) PAVE360 shifts SDV development left by enabling pre-silicon software validation and real-time sync with physical vehicles. 2) A visual map of Synopsys’ capabilities: Electronics digital twins are enabled across different abstraction levels: From early-stage algorithm modeling through to full binary deployment on physical ECUs (source: IoT Analytics at EW2025)
Key analysis from the MWC and EW 2025 events report:
“Virtual platforms have advanced to the point where they can effectively replace early-stage hardware in critical development workflows, changing how MCUs and automotive ECUs are designed and brought to market. This reflects a mature and increasingly silicon-independent development model. One of the most notable announcements came from NXP, which introduced its new S32K5 MCU without presenting any physical silicon, using Synopsys’ Virtualizer for early pre-silicon software development. Green Hills Software demonstrated its stack running on the S32K5 virtual prototype, showing how ecosystem partners can validate and integrate software early.”
5. Cybersecurity: CRA compliance becoming an important topic as post-quantum solutions emerge
Cybersecurity took center stage at MWC and EW 2025, driven by two forces: the regulatory push from the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) and the looming threat of quantum computing undermining traditional encryption methods.
EU CRA-driven security-by-design is reshaping the embedded and IoT ecosystem. At EW 2025 , US-based electronic components manufacturer Arrow Electronics demonstrated CRA-compliant device stacks that integrate secure provisioning, attestation, and OTA firmware validation. These demos underscored that device security must now be natively embedded into every stage of the product lifecycle, from manufacturing to field operations.
However, during an in-depth conversation with IoT Analytics, an Infineon representative noted that much of the industry still lacks full awareness of the CRA and its implications for business operations:
“The knowledge of the people that showed interest in our CRA exhibit was very low. People are neither aware of roll-out timelines, nor what CRA entails. I was surprised to see that many people thought that CRA only targets some components. It encompasses all communications components of devices.”
CRA representative at the Infineon Technologies AG
Post-quantum cryptography is also gaining momentum, particularly for securing network transport layers. At MWC 2025, Italy-based multinational telecommunications company TI Sparkle and UK-based cybersecurity company Arqit unveiled a quantum-safe network-as-a-service solution that uses Arqit’s quantum-safe VPN (or QSVPN) to secure internet communications. The solution employs a unique self-generated key agreement model, ensuring end-to-end control and eliminating traditional key exchanges, offering quantum-safe encryption and continuous key rotation.
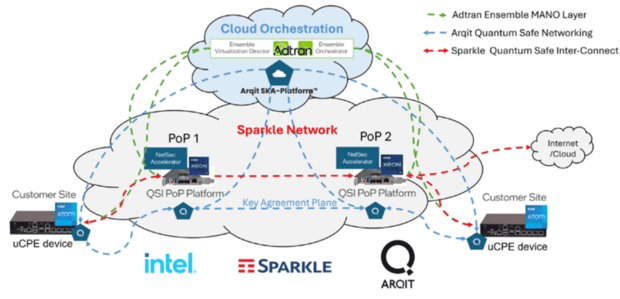
Intel and Arqit demonstrated Sparkle’s Quantum-Safe Inter-Connect, combining quantum-safe networking for secure, scalable data transfers between customer sites and Sparkle’s network with end-to-end encryption and key management (source: IoT Analytics at MWC 2025)
Analyst takeaway : The future of secure connectivity and computing is being redefined at the system level
The developments seen by the IoT Analytics team at MWC 2025 and EW 2025 show that secure connectivity and computing are no longer isolated advancements—they are being fundamentally redesigned across the stack.
Networks are becoming intelligent and autonomous with AI embedded into RAN infrastructure. Edge computing is evolving to support multimodal AI workloads with full lifecycle integration.
Satellite technologies are no longer secondary links but primary components of industrial and critical network design. Automotive computing platforms are shifting from hardware-defined systems to software-defined architectures validated entirely through digital twin environments. Finally, cybersecurity—driven by regulation and quantum-era threats—is being built into devices, networks, and applications by design.
Across all sectors, the traditional boundaries between communication, computation, and security are dissolving—giving rise to intelligent, secure, and resilient infrastructure that is ready for the next wave of digital transformation.
Disclosure
Companies mentioned in this article—along with their products—are used as examples to showcase market developments. No company paid or received preferential treatment in this article, and it is at the discretion of the analyst to select which examples are used. IoT Analytics makes efforts to vary the companies and products mentioned to help shine attention to the numerous IoT and related technology market players.
It is worth noting that IoT Analytics may have commercial relationships with some companies mentioned in its articles, as some companies license IoT Analytics market research. However, for confidentiality, IoT Analytics cannot disclose individual relationships. Please contact compliance@iot-analytics.com for any questions or concerns on this front.
More information and further reading
Are you interested in learning more about generative AI applications and projects?

Mobile World Congress and Embedded World 2025—Analyst Takeaways
A comprehensive summary of the key highlights from Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025 and Embedded World 2025– including 23 in-depth insights, highlights from closed-door conference sessions, an edge AI comparison of 5 prominent chipset and module vendors- assembled by the IoT Analytics analyst team.
Already a subscriber? View your reports here →
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- The top 10 enterprise generative AI applications – Based on 530 real-world projects
- State of private 5G in 2024: Key growth trends, use cases, and forecast
- The rise of smart and AI-capable cellular IoT modules: Evolution and market outlook
- The top 6 edge AI trends—as showcased at Embedded World 2024
- Top 10 IoT & telco trends—as seen at MWC 2024
Related publications
You may also be interested in the following reports:
- 5G IoT & Private 5G Market Report 2024–2030
- Generative AI Market Report 2025-2030
- List of Generative AI Projects 2025
Related market trackers
You may be interested in the following trackers:
- Cellular IoT Connectivity Tracker and Forecast
Subscribe to our research newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports, including dedicated analyst time, check out the Enterprise subscription.
Leave a Comment